题目描述:
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up (u), down (d), left (l) or right (r), but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction. There is also a hole in this maze. The ball will drop into the hole if it rolls on to the hole.
Given the ball position, the hole position and the maze, your job is to find out how the ball could drop into the hole by moving shortest distance in the maze. The distance is defined by the number of empty spaces the ball go through from the start position (exclude) to the hole (include). Output the moving directions by using 'u', 'd', 'l' and 'r'. Since there may have several different shortest ways, you should output the lexicographically smallest way. If the ball cannot reach the hole, output "impossible".
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The ball and hole coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
Example 1
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 Input 2: ball coordinate (rowBall, colBall) = (4, 3) Input 3: hole coordinate (rowHole, colHole) = (0, 1) Output: "lul" Explanation: There are two shortest ways for the ball to drop into the hole. The first way is left -> up -> left, represented by "lul". The second way is up -> left, represented by 'ul'. Both ways have shortest distance 6, but the first way is lexicographically smaller because 'l' < 'u'. So the output is "lul".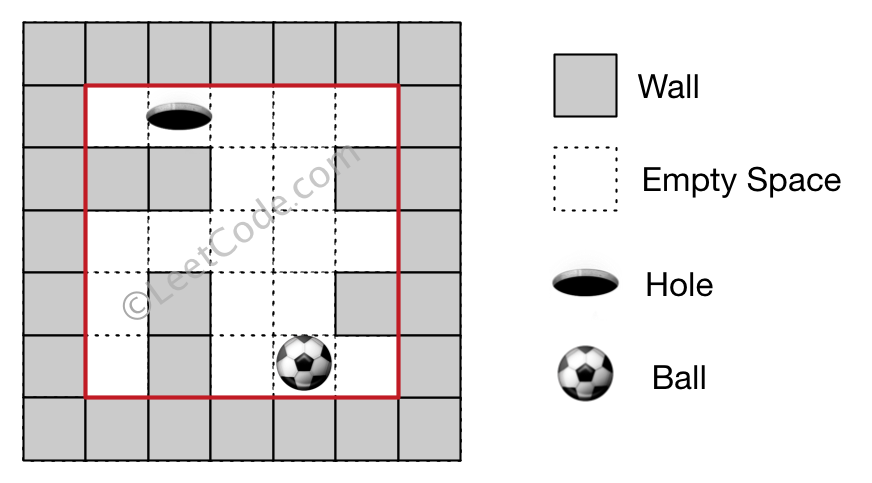
Example 2
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 Input 2: ball coordinate (rowBall, colBall) = (4, 3) Input 3: hole coordinate (rowHole, colHole) = (3, 0) Output: "impossible" Explanation: The ball cannot reach the hole.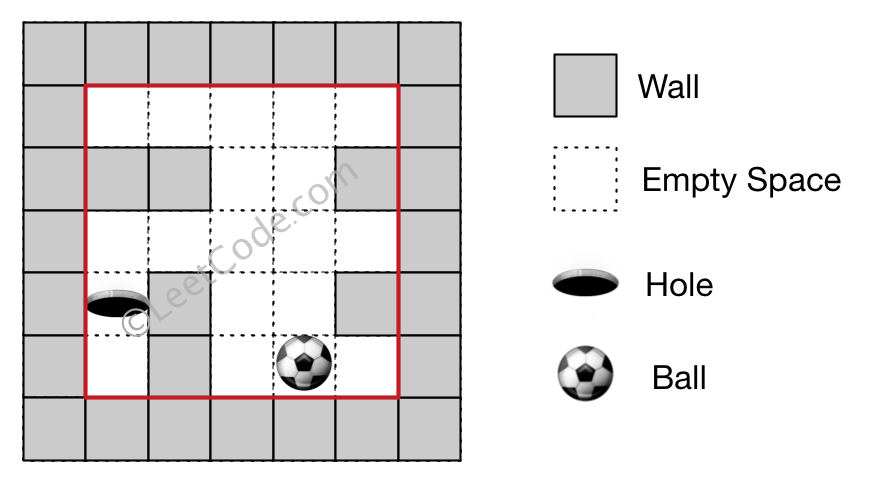
Note:
- There are only one ball and one hole in the maze.
- The ball and hole will only exist in the empty space, and they will not at the same position initially.
- The given maze doesn't contain border (like the red rectangle in the example pictures), but you should assume the border of the maze are all walls.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces, and the length and width of the maze won't exceed 30.
题目大意:
给定一个二维迷宫,其中包含一个小球和一个洞。小球可以向上(u)、下(d)、左(l)、右(r)四个方向移动。每当小球选择一个方向后,会持续移动直到遇到墙壁为止。小球经过洞时会落入洞中。
给定小球的初始位置ball,洞的位置hole。二维迷宫maze中1表示墙壁,0表示空地,四周被墙壁包围。求小球到洞的最短路径,如果存在距离相等的多条路径,返回字典序最短的那条。
注意:
- 球和洞各只有1个。
- 球和洞只存在于空地上,并且初始位置不同。
- 给定的迷宫不包含边界,但迷宫四周都是墙壁。
- 迷宫至少包含两个空地,并且迷宫的长度和宽度不超过30。
解题思路:
预处理 + 单源最短路
首先预处理迷宫maze中各点坐标向四个方向运动最终可以达到的坐标,用数组dmap记录。 例如dmap[(3, 2)]['u']表示从坐标(3, 2)出发向上运动最终可以到达的位置。 利用数组bmap记录迷宫中各点坐标到小球初始位置的最短距离dist与最短路径path。 维护队列queue,初始将(ball, 0, '')加入queue(坐标,距离,路径) 记当前坐标为p,从p出发,分别向u, d, l, r四个方向扩展并更新下一个坐标np的最短距离与路径,保存在bmap中。 如果np得到更新,则将np加入队列;重复此过程直到queue为空 返回bmap[hole]
Python代码:
class Solution(object):
def findShortestWay(self, maze, ball, hole):
"""
:type maze: List[List[int]]
:type ball: List[int]
:type hole: List[int]
:rtype: str
"""
ball, hole = tuple(ball), tuple(hole)
dmap = collections.defaultdict(lambda: collections.defaultdict(int))
w, h = len(maze), len(maze[0])
for dir in 'dlru': dmap[hole][dir] = hole
for x in range(w):
for y in range(h):
if maze[x][y] or (x, y) == hole: continue
dmap[(x, y)]['u'] = dmap[(x - 1, y)]['u'] if x > 0 and dmap[(x - 1, y)]['u'] else (x, y)
dmap[(x, y)]['l'] = dmap[(x, y - 1)]['l'] if y > 0 and dmap[(x, y - 1)]['l'] else (x, y)
for x in range(w - 1, -1, -1):
for y in range(h - 1, -1, -1):
if maze[x][y] or (x, y) == hole: continue
dmap[(x, y)]['d'] = dmap[(x + 1, y)]['d'] if x < w - 1 and dmap[(x + 1, y)]['d'] else (x, y)
dmap[(x, y)]['r'] = dmap[(x, y + 1)]['r'] if y < h - 1 and dmap[(x, y + 1)]['r'] else (x, y)
bmap = {ball : (0, '')}
distance = lambda pa, pb: abs(pa[0] - pb[0]) + abs(pa[1] - pb[1])
queue = collections.deque([(ball, 0, '')])
while queue:
front, dist, path = queue.popleft()
for dir in 'dlru':
if dir not in dmap[front]: continue
np = dmap[front][dir]
ndist = dist + distance(front, np)
npath = path + dir
if np not in bmap or (ndist, npath) < bmap[np]:
bmap[np] = (ndist, npath)
queue.append((np, ndist, npath))
return bmap[hole][1] if hole in bmap else 'impossible'
下面的解法采用Dijkstra算法,比上面的解法效率更优。
Python代码:
class Solution(object):
def findShortestWay(self, maze, ball, hole):
"""
:type maze: List[List[int]]
:type ball: List[int]
:type hole: List[int]
:rtype: str
"""
ball, hole = tuple(ball), tuple(hole)
dmap = collections.defaultdict(lambda: collections.defaultdict(int))
w, h = len(maze), len(maze[0])
for dir in 'dlru': dmap[hole][dir] = hole
for x in range(w):
for y in range(h):
if maze[x][y] or (x, y) == hole: continue
dmap[(x, y)]['u'] = dmap[(x - 1, y)]['u'] if x > 0 and dmap[(x - 1, y)]['u'] else (x, y)
dmap[(x, y)]['l'] = dmap[(x, y - 1)]['l'] if y > 0 and dmap[(x, y - 1)]['l'] else (x, y)
for x in range(w - 1, -1, -1):
for y in range(h - 1, -1, -1):
if maze[x][y] or (x, y) == hole: continue
dmap[(x, y)]['d'] = dmap[(x + 1, y)]['d'] if x < w - 1 and dmap[(x + 1, y)]['d'] else (x, y)
dmap[(x, y)]['r'] = dmap[(x, y + 1)]['r'] if y < h - 1 and dmap[(x, y + 1)]['r'] else (x, y)
bmap = {ball : (0, '', ball)}
vset = set()
distance = lambda pa, pb: abs(pa[0] - pb[0]) + abs(pa[1] - pb[1])
while bmap:
dist, path, p = min(bmap.values())
if p == hole: return path
del bmap[p]
vset.add(p)
for dir in 'dlru':
if dir not in dmap[p]: continue
np = dmap[p][dir]
ndist = dist + distance(p, np)
npath = path + dir
if np not in vset and (np not in bmap or (ndist, npath, np) < bmap[np]):
bmap[np] = (ndist, npath, np)
return 'impossible'
本文链接:http://bookshadow.com/weblog/2017/01/29/leetcode-the-maze-ii/
请尊重作者的劳动成果,转载请注明出处!书影博客保留对文章的所有权利。
